Saturday, August 2, 2008
Start Menu ++
Labels: Vista Addon
Posted by Vicky at 9:00 PM 0 comments
Use BitLocker Drive Encryption without TPM chip
Windows Vista includes a new hard drive encryption feature called BitLocker Drive Encryption. BitLocker can be a very useful security feature for businesses and home users that have sensitive and confidential information stored on their computer. Unfortunately, BitLocker Drive Encryption by default requires a Trusted Platform Module (TPM Chip) version 1.2 or later installed in your computer. A lot of the computers and laptops on the market do not come with TPM chips installed since they are typically only found in premium model business computers. If you have Windows Vista Business, Ultimate or Enterprise but do not have a TPM chip, you can still use BitLocker Drive Encryption.Hidden away in local group policy is a setting that will allow you to turn on the ability to use a USB storage device instead of a TPM key to store the encryption key. This is a great feature for users that don't have the latest high-end hardware because you can still use hard drive encryption. However, every time you turn on your computer, the USB storage device that has the encryption key located on it must be plugged in. Without it, your computer will not boot up. One BitLocker Drive Encryption is setup with a USB storage device, that USB storage device basically becomes the key to your computer.Press the Windows button, type gpedit.msc and press Enter. Navigate through: Computer Policy, Administrative Templates, Windows Components and BitLocker Drive Encryption. Right click on Control Panel Setup: Enable advanced startup options and select Properties. Check Enabled and click OK.
Labels: Vista Fixes
Posted by Vicky at 8:48 PM 0 comments
Thursday, July 3, 2008
Vista Secret Folder
This is not a registry hack. We are merely using the registry to discover CLSIDs (Class Identifiers).
The idea behind this tip is to create a folder which is invisible to the Vista indexer. Please be aware that the files are neither encrypted, nor hidden from anyone looking with Windows Explorer. To my mind this limitation confines the usefulness of this tip to special situations. However, from a learning point of view this tip is most instructive.
Topics for Vista's Secret Folder
Instructions to Create a Secret Folder
For your files to remain hidden, this secret folder needs a special extension .{26EE0668-A00A-44D7-9371-BEB064C98683}.
Create a normal folder, for example stuff. Now rename it with this special CLSID (Class ID) extension. For this trick to work, remember both the dot and the curly brackets.
stuff.{26EE0668-A00A-44D7-9371-BEB064C98683}
Testing your hidden files
Create a file inside your folder with the .{26EE0668-A00A-44D7-9371-BEB064C98683} extension. For example 'Guy Stuff.doc'. Now search for Guy Stuff.doc. You should get a negative result, Vista's search will ignore files in this folder.
Just in case you believe this negative result is due to slow indexing, create another document in a regular folder, search for that document. This time you should have a positive result.
There is a fancy variation of my tip using a different clsid extension. I say fancy, because it creates a Recycle Bin folder
.{645FF040-5081-101B-9F08-00AA002F954E}
Labels: Vista Fixes
Posted by Vicky at 3:53 AM 0 comments
Speed Start menu Search
Speed-Up Windows Vista's Start Menu SearchWhen you perform a search using the search box in the start panel, Windows Vista automatically searches the file index as well. The file index can be quite large because it includes all the files on your hard drive. One way to speed-up searching in your Start Menu applications is to narrow the scope of the search so that it does not include files on the hard drive:
Method 1: Registry Hack1.
Open registry editor using regedit.
2. Navigate to HKEY_CURRENT_USER > Software > Microsoft > Windows > CurrentVersion > Explorer and select Advanced.
3. Find and right-click on Start_SearchFiles and select Modify.
4. Set the Value to 0.
5. Restart the Explorer.exe process or reboot the computer.
Method 2: Start Button1. Right-click on the Start Button and select Properties.
2. Click on the Customize button.
3. Uncheck Search Communications.
4. Set Search Files to Don't Search for files.
5. Click OK.
Labels: Vista Fixes
Posted by Vicky at 3:50 AM 0 comments
Increase SATA Disk Drive Performance
You can squeeze a more performance out of your SATA hard disk drive by enabling write caching. The price though, is an increased risk for data loss/corruption should you experienced a power loss - this risk is less in a laptop because of its battery:
1. Click on the Start Button, enter Device Manager and hit Enter.
2. Expand Disk Drives.
3. Right-click on your hard disk drive and select Properties.
4. On the Policies tab, check Enable Advanced Performance.
5. Click OK and close Device Manager.
Labels: Vista Fixes
Posted by Vicky at 3:49 AM 0 comments
Sunday, June 29, 2008
Force Readyboost in Windows Vista
Although I have tested this with my USB without damaging it, I am in no way responsible for what happens to your removable device when testing this out. Just make sure you follow the instructions carefully. Also, expect little or no performance gain when using this on incompatible devices.
1. Plug in the device.
2. Access your device properties: Start Pearl > My Computer > Right click device > Properties > Readyboost Tab
3. Select, “Stop retesting this device when I plug it in.”
4. Unplug the device.
5. Open the registry editor: Start Pearl > Type regedit in the search bar
6. Access: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE / SOFTWARE / Microsoft / Windows-NT / CurrentVersion / EMDgmt
7. Make the following registry changes:
- Change the Device Status to 2.
- Change ReadSpeedKBs to 1000.
- Change WriteSpeedKBs to 1000.
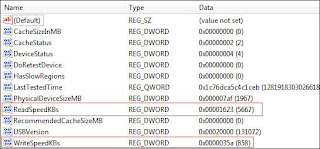 8. Plug in the device and Readyboost should work
8. Plug in the device and Readyboost should workLabels: Vista Fixes
Posted by Vicky at 9:09 PM 0 comments
Internet Explorer Tweak
Internet Explorer 7 only allows you to download two files from the same server at a time. This is not a software limit but rather a limit imposed based on the web standard. Since this is simply a software setting, it can be modified and you can increase the limit to something much high such as 10. Follow the steps below to increase your max downloads from the same server:
1. Click on the Start Button and type in Regedit.
2. When Registry Editor loads navigate through HKEY_CURRENT_USER, Software, Microsoft, Windows, CurrentVersion and Internet Settings.
3. Right click on MaxConnectionsPerServer and select Modify. Set the decimal value to something greater than 2.
4. Right click on MaxConnectionsPer1_0Server and select Modify. Set the decimal value to something greater than 2.
5. Reboot.
Labels: Internet Tweak
Posted by Vicky at 6:38 AM 0 comments
Friday, June 27, 2008
Re-enabling hibernation in Windows Vista after disk cleanup
Windows Vista Cleanup tool, which enables you to clear your disk of unnecessary files, one of the main reason why we run out of space on C:\ partition.
After having cleanup the files I cannot see the Hibernate option in Power Options anymore.This problem occurs when the Disk Cleanup Tool disables the hibernation file. The hibernation file must be enabled to access the hybrid sleep feature and the hibernation feature in Windows Vista. When the hibernation file is disabled, and the hybrid sleep feature is enabled, a backup of open programs and open files will not be saved to the disk when you use the sleep feature in Windows Vista. Additionally, if the computer loses power while the Windows is in sleep mode, open programs and open files will not be recovered, and any unsaved work will be lost.
In order to get the Hibernate option back in the Power Options mode you should take following steps:
1. Click Start , click All Programs, and then click Accessories.
2. Right-click Command Prompt, click Run as administrator, type powercfg -h on, and then press ENTER.
The command line tool powercfg.exe enables users to control the power settings on the system. An overview of all parameters that can be passed to the cool can be found by running the command "C:\Windows\system32>powercfg /?" from the command prompt.
For the hibernation we need the following:
-HIBERNATE, -H
Usage: POWERCFG -H
After running the command above with the hibernation parameter - powercfg -h - the problem is solved and I can again hibernate my Windows Vista system. This applies to all Windows Vista editions.
Labels: Vista Fixes
Posted by Vicky at 8:11 PM 0 comments
Wednesday, June 25, 2008
NTLDR Issue
Ever got this message while booting? NTLDR is Missing.
Some think the drive has crashed and formatting is the only way. Here is a way to deal with that problem.
Below are the full error messages that may be seen when the computer is booting.
NTLDR is MissingPress any key to restartBoot: Couldn't find NTLDRPlease insert another diskNTLDR is missing Press Ctrl Alt Del to Restart
Cause: Computer is booting from a non-bootable source. Computer hard disk drive is not properly setup in BIOS. Corrupt NTLDR and/or NTDETECT.COM file. Misconfiguration with the boot.ini file. Attempting to upgrade from a Windows 95, 98, or ME computer that is using FAT32. New hard disk drive being added. Corrupt boot sector / master boot record. Seriously corrupted version of Windows 2000 or Windows XP. Loose or Faulty IDE/EIDE hard disk drive cable. Solutions:
Computer is booting from a non-bootable sourceMany times this error is caused when the computer is attempting to boot from a non-bootable floppy disk or CD-ROM. First verify that no floppy diskette is in the computer, unless you are attempting to boot from a diskette.
If you are attempting to boot from a floppy diskette and are receiving this error message it is likely that the diskette does not have all the necessary files and/or is corrupt.
If you are attempting to install Windows XP or Windows 2000 and are receiving this error message as the computer is booting verify that your computer BIOS has the proper boot settings. For example, if you are attempting to run the install from the CD-ROM make sure the CD-ROM is the first boot device, and not the hard disk drive.
Second, when the computer is booting you should receive the below prompt.
Press any key to boot from the CD
Important: When you see this message press any key such as the Enter key immediately, otherwise it will try booting from the hard drive and likely get the NTLDR error again.
Note: If you are not receiving the above message and your BIOS boot options are set properly it's also possible that your CD-ROM drive may not be booting from the CD-ROM properly. Verify the jumpers are set properly on the CD-ROM drive. Additional information about checking the CD-ROM drive connections can be found on document CH000213.
Additional information: This error has also been known to occur when a memory stick is in a card reader and the computer is attempting to boot from it. If you have any type of card reader or flash reader make sure that no memory stick is inside the computer.
Computer hard disk drive is not properly setup in BIOS
Verify that your computer hard disk drive is properly setup in the BIOS / CMOS setup. Improper settings can cause this error. Additional information on how to enter the BIOS / CMOS setup can be found in document CH000192.
Corrupt NTLDR and/or NTDETECT.COM file
Windows 2000 users
If your computer is using Microsoft Windows 2000 and you are encountering the NTLDR error. Create the below boot.ini file on the floppy diskette drive.
[boot loader]timeout=30default=multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)\WINNT[operating systems]multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)\WINNT="Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional" /fastdetect
Copy the NTLDR and NTDETECT.COM files from another computer using the same Operating System. Both of these files are located in the root directory of the primary hard disk drive. For example, C:\NTLDR and C:\NTDETECT.COM should be the locations of these files on many computers.
Please keep in mind that these files are hidden system files, if you need additional help with viewing hidden files in Windows please see document CH000516. Once these files have been copied to a floppy diskette reboot the computer and copy the NTLDR and NTDETECT.COM files to the root directory of the primary hard disk drive. Below is an example of what commonly should be performed from the A:\> drive.
copy ntldr c:copy ntdetect.com c:
After the above two files have been copied, remove the floppy diskette and reboot the computer.
Windows XP users
Insert the Windows XP bootable CD into the computer. When prompted to press any key to boot from the CD, press any key. Once in the Windows XP setup menu press the "R" key to repair Windows. Log into your Windows installation by pressing the "1" key and pressing enter. You will then be prompted for your administrator password, enter that password. Copy the below two files to the root directory of the primary hard disk. In the below example we are copying these files from the CD-ROM drive letter "E". This letter may be different on your computer.
copy e:\i386\ntldr c:\copy e:\i386\ntdetect.com c:\
Once both of these files have been successfully copied, remove the CD from the computer and reboot. Misconfiguration with the boot.ini file
Edit the boot.ini on the root directory of the hard disk drive and verify that it is pointing to the correct location of your Windows Operating System and that the partitions are properly defined. Additional information about the boot.ini can be found on document CH000492.
Attempting to upgrade from a Windows 95, 98, or ME computer that is using FAT32
If you are getting this error message while you are attempting to upgrade to Windows 2000 or Windows XP from Windows 95, Windows 98, or Windows ME running FAT32 please try the below recommendations.
Boot the computer with a Windows 95, Windows 98 or Windows ME bootable diskette. At the A:\> prompt type:
sys c:
After pressing enter you should receive the "System Transferred" message. Once this has been completed remove the floppy diskette and reboot the computer. New hard disk drive being added
If you are attempting to add a new hard disk drive to the computer make sure that drive is a blank drive. Adding a new hard disk drive to a computer that already has Windows installed on it may cause the NTLDR error to occur.
If you are unsure if the new drive is blank or not try booting from a bootable diskette and format the new hard disk drive.
Corrupt boot sector / master boot record
It's possible your computer's hard disk drive may have a corrupt boot sector and/or master boot record. These can be repaired through the Microsoft Windows Recovery console by running the fixboot and fixmbr commands.
Additional information and help in getting into the Microsoft Windows Recovery console can be found on document CH000627.
Seriously corrupted version of Windows 2000 or Windows XP
If you have tried each of the above recommendations that apply to your situation and you continue to experience this issue it is possible you may have a seriously corrupted version of Microsoft Windows. Therefore we would recommend you reinstall Microsoft Windows 2000 and Windows XP.
If you are encountering this issue during your setup you may wish to completely erase your computer hard disk drive and all of its existing data and then install Microsoft Windows 2000 / Windows XP. Additional information about erasing the computer and starting over can be found on document CH000186.
Loose or Faulty IDE/EIDE hard disk drive cable
This issue has been known to be caused by a loose or fault IDE/EIDE cable. If the above recommendation does not resolve your issue and your computer hard disk drive is using an IDE or EIDE interface. Verify the computer hard disk drive cable is firmly connected by disconnected and reconnecting the cable.
If the issue continues it is also a possibility that the computer has a faulty cable, try replacing the hard disk drive cable with another cable and/or a new cable.
Labels: NTLDR missing
Posted by Vicky at 10:01 PM 0 comments
Hide All Desktop Icons
Ever wished your desktop is clean without icons forever? Here's the deal.
Click Start-Run-and type 'regedit' Browse to:
Hive: HKEY_CURRENT_USERKey: Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\ExplorerName: NoDesktop Type: REG_DWORDValue: 1
With this key enabled, in addition, you cannot right click on the desktop to get a context menu. This is a lockdown option.
Almost all Windows NT registry hacks work for Windows 2000 and Windows XP. Windows NT and Windows XP have the Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explorer key by default. Windows 2000 does not. But if you create the key with the NoDesktop value set to 1, the hack works for Windows 2000 also. When you create the Explorer key under Policies, you will be prompted for a class. Leave it blank.
To hide all Desktop Icons from Explorer but still enable right-clicking on the desktop there is the following registry hack :
Hive: HKEY_CURRENT_USERKey: Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\AdvancedName: HideIcons Type: REG_DWORDValue: 1
Labels: Hide Desktop Icon
Posted by Vicky at 3:04 AM 1 comments